End-use electrification and its impact on distribution systems

In what ways will utilities need to upgrade the electric distribution grid to accommodate electrified loads, and what will those upgrades cost? Our study focuses on the PG&E service area in Northern California, which serves 4.8 million electricity customers and is subject to aggressive targets for both EV adoption and electrification of residential space and […]
Embarking on the Great Implementation: What I learned during 16 months at the California Energy Commission

Location: 1605 Tilia Street, Suite 100, Davis, CA Watch Video Join us for an enlightening seminar featuring Ben Finkelor, Executive Director of UC Davis Energy and Efficiency Institute (EEI), as he shares insights and experiences gained during his 16-month tenure as a Senior Advisor and Chief of Staff to Vice Chair Siva Gunda at the […]
Energy Graduate Group: Contact Us
Request More Information Tell us about yourself. Please complete the following fields to help us send information relevant to you. * Indicates required fields
Energy Waste in Empty Buildings and How to Reduce It

Office vacancy rates in the United States recently surpassed 20 percent for the first time in decades. Even where offices are leased, they are underutilized. Attendance is significantly reduced and many buildings that were once bustling five days a week might now be largely empty much of the time. Yet, despite this reduced occupancy, the energy consumption in these buildings remains surprisingly high.
A Path Forward: Decarbonizing Concrete Production
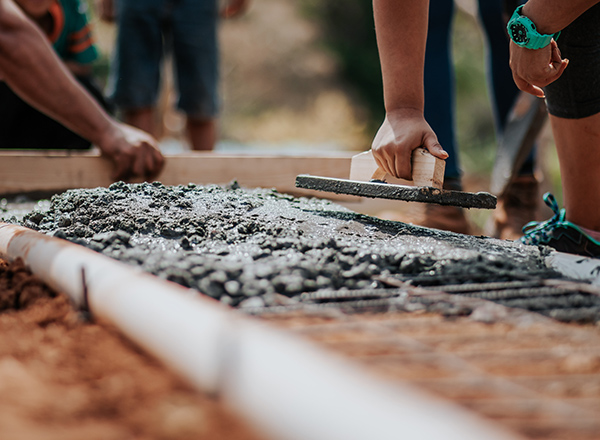

Concrete, the backbone of California’s infrastructure, is undergoing a transformation. The need for sustainable construction practices is increasingly urgent.
EEI Brings Industrial Decarbonization Concepts to India Conference
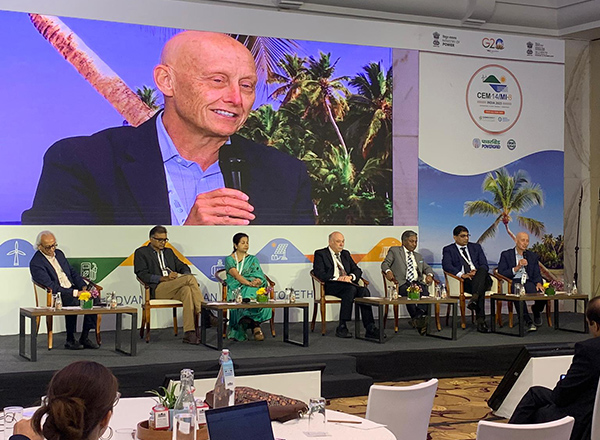

EEI Faculty Director, Kelly Kissock, participated in a global conference of clean energy leaders in Goa, India. Kelly presented at a panel on international cooperation for a resilient and decarbonized building sector, in which he shared insights on California’s net-zero energy Title 24 building energy-efficiency code.
Sustainable Systems Science for Accelerating Clean Energy Transitions and Climate Solutions
Location: 1605 Tilia Street, Suite 100, Davis, CA Watch Video The next few years are critical. Immediate and deep reductions in greenhouse gas emissions are necessary across all sectors or limiting warming to 1.5 °C will be beyond reach. Sustainable systems science provides a useful framework and tools to characterize mobility, buildings, food, and other […]
New Wine in Old Bottle: Evolution of the Texas Electricity Market Since 2021 Blackouts and Broader Electricity System Implications

In February 2021 winter storm Uri left hundreds dead and tens of billions of dollars in losses in Texas. This talk will take an integrative stock of the lessons and insights that have emerged regarding the functioning of the ERCOT electricity market in the aftermath of Uri. By examining the nature of recent changes in […]
Student Job Opening: Graphic Design // Creative Specialist
Motivated to tell stories through visual communications? The Energy and Efficiency Institute (EEI) at the University of California, Davis, is seeking a graphic designer/creative specialist student to put their design skills to work assisting EEI’s Creative Specialist. Guided by EEI’s Creative Specialist, this position requires a student with a desire and motivation to learn and […]
EEI Seeking Post-Doctoral Researcher for Materials Decarbonization
The Energy and Efficiency Institute at the University of California, Davis, is seeking one post-doc to lead research in the area of low-carbon materials. The post-doc will participate in, lead, and develop new research projects in designing sustainable materials with an emphasis on assessing environmental burdens and integrating environmental impact assessment methods with material performance.

